Dr. CHAN Loi-yuen, Dr. KU Lap-shing, Simon & Dr. TANG Yuk-ming, William
Specialist in Dermatology & Venereology
皮膚科病例研究之內容誠蒙陳來源醫生、顧立誠醫生及鄧旭明醫生提供。
Online Clinical Case Study (November 2005)
The content of the Office Cardiology Series is provided by:
Dr. Li Siu Lung, Steven
M.B.,B.S.(H.K.),M.R.C.P.(U.K.),F.H.K.A.M.,F.H.K.C.P.,F.R.C.P.(Glasg.),F.R.C.P. (Edin.),Specialist in Cardiology
Dr. Wong Shou Pang, Alexander
F.R.C.P.,F.H.K.A.M.(Med.),F.H.K.C.P.,Specialist in Cardiology
臨床心臟科個案研究之內容誠蒙李少隆醫生及王壽鵬醫生提供。
Anticoagulation with warfarin
Answers
| 1. |
Warfarin exerts its effect via inhibition of clotting factors II, VII, IX, X. |
|
True |
|
|
|
|
| 2. |
Warfarin effect takes place in 6 hours after administration. |
|
False |
|
|
|
|
| 3. |
Warfarin does not cross placental barrier. |
|
False |
|
|
|
|
| 4. |
Warfarin's effect is potentiated with amiodarone. |
|
True |
|
|
|
|
|
1. Warfarin exerts its effect by inhibiting the hepatic synthesis of vitamin K dependent clotting factors II, VII, IX and X; which is caused by the inhibition of vitamin K. The effect of warfarin is monitored with prothrombin time, which is usually kept at 2-3 times control for most therapeutic indications. 2. After oral administration, warfarin is absorbed erratically from the gastrointestinal tract, after which the molecules are almost entirely bound to plasma protein. There is a 2 to 7 days of delay between the achievement of a peak plasma level and a substantial therapeutic response. The half-life is around 37 hours. Normally a loading dose is used if early achievement of therapeutic response is desired. For Chinese, the usual maintenance dose is 2 to 3mg daily but it may vary from 1 to 20mg daily. Therefore titration of doses according to regular monitoring of the prothrombin time is essential. Patients with heart failure, liver disease and renal impairment require a lower maintenance dose. In general, PT/INR monitoring every 4-8 weeks is needed for patients on long term warfarin treatment. Patients should be reminded that warfarin should be stopped a few days before dental or surgical procedures. Patient education is an integral part of warfarin program and patients need to know the different warfarin tablet preparations and protocol of dosage titration. They should be reminded for symptoms of bleeding tendency. 3. Warfarin, in contrast to heparin, crosses placental barrier. Since it is teratogenic to the fetus, warfarin, if indicated for the pregnant woman, is generally omitted in the first 8 weeks of pregnancy, in which heparin is used for replacement. 4. Warfarin is metabolized in the liver and its potency is markedly affected by diet as well as concomitantly administered medications. Its effects would be reduced with many dark green vegetables that are rich in vitamin K and with drugs that induce hepatic enzymes such as barbiturates, phenytoin and rifampin. On the other hand, its effects are potentiated by those drugs that inhibit the CYP 2C9 isoform of the hepatic cyotchrome P-450 system. These include amiodarone, metronidazole, co-trimoxazole, anti-fungals like fluconazole and cimetidine. Other potentiating drugs include allopurinol, propafenone and quinidine. Patients should be reminded that they should not take any concomitant herbal medicine or drugs of uncertain nature while they are on warfarin treatment. |
|
| Back to top |
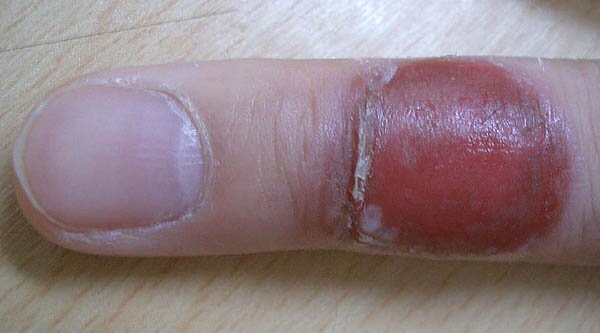
A 35 year old male presented with recurrent skin rash over his left middle finger. There were totally three episodes of painful erythema which developed into blister shortly afterward. He noticed an association between the skin lesion and his joint pain for which naproxen has been prescribed by his family doctor. Physical examination revealed a one cm diameter superficial eroded lesion.

|
| The content of the Dermatology Series is provided by: Dr. CHAN Loi-yuen, Dr. KU Lap-shing, Simon & Dr. TANG Yuk-ming, William Specialist in Dermatology & Venereology 皮膚科病例研究之內容誠蒙陳來源醫生、顧立誠醫生及鄧旭明醫生提供。 |
Answers